-
About Streets
- Introduction
- Defining Streets
-
Shaping Streets
- The Process of Shaping Streets
- Aligning with City and Regional Agendas
- Involving the Right Stakeholders
- Setting a Project Vision
- Communication and Engagement
- Costs and Budgets
- Phasing and Interim Strategies
- Coordination and Project Management
- Implementation and Materials
- Management
- Maintenance
- Institutionalizing Change
- Measuring and Evaluating Streets
-
Street Design Guidance
- Designing Streets for Great Cities
- Designing Streets for Place
-
Designing Streets for People
- Utilities and Infrastructure
- Operational and Management Strategies
- Design Controls
-
Street Transformations
- Streets
-
Intersections
- Intersection Design Strategies
- Intersection Analysis
- Intersection Redesign
- Mini Roundabout
- Small Raised Intersection
- Neighborhood Gateway Intersection
- Intersection of Two-Way and One-Way Streets
- Major Intersection: Reclaiming the Corners
- Major Intersection: Squaring the Circle
- Major Intersection: Cycle Protection
- Complex Intersection: Adding Public Plazas
- Complex Intersection: Improving Traffic Circles
- Complex Intersection: Increasing Permeability
- Resources
Global Street Design Guide
-
About Streets
- Introduction
- Defining Streets
-
Shaping Streets
Back Shaping Streets
- The Process of Shaping Streets
- Aligning with City and Regional Agendas
- Involving the Right Stakeholders
- Setting a Project Vision
- Communication and Engagement
- Costs and Budgets
- Phasing and Interim Strategies
- Coordination and Project Management
- Implementation and Materials
- Management
- Maintenance
- Institutionalizing Change
-
Measuring and Evaluating Streets
Back Measuring and Evaluating Streets
-
Street Design Guidance
-
Designing Streets for Great Cities
Back Designing Streets for Great Cities
-
Designing Streets for Place
Back Designing Streets for Place
-
Designing Streets for People
Back Designing Streets for People
- Comparing Street Users
- A Variety of Street Users
-
Designing for Pedestrians
Back Designing for Pedestrians
- Designing for Cyclists
-
Designing for Transit Riders
Back Designing for Transit Riders
- Overview
- Transit Networks
- Transit Toolbox
-
Transit Facilities
Back Transit Facilities
-
Transit Stops
Back Transit Stops
-
Additional Guidance
Back Additional Guidance
-
Designing for Motorists
Back Designing for Motorists
-
Designing for Freight and Service Operators
Back Designing for Freight and Service Operators
-
Designing for People Doing Business
Back Designing for People Doing Business
-
Utilities and Infrastructure
Back Utilities and Infrastructure
- Utilities
-
Green Infrastructure and Stormwater Management
Back Green Infrastructure and Stormwater Management
-
Lighting and Technology
Back Lighting and Technology
-
Operational and Management Strategies
Back Operational and Management Strategies
- Design Controls
-
Street Transformations
-
Streets
Back Streets
- Street Design Strategies
- Street Typologies
-
Pedestrian-Priority Spaces
Back Pedestrian-Priority Spaces
-
Pedestrian-Only Streets
Back Pedestrian-Only Streets
-
Laneways and Alleys
Back Laneways and Alleys
- Parklets
-
Pedestrian Plazas
Back Pedestrian Plazas
-
Pedestrian-Only Streets
-
Shared Streets
Back Shared Streets
-
Commercial Shared Streets
Back Commercial Shared Streets
-
Residential Shared Streets
Back Residential Shared Streets
-
Commercial Shared Streets
-
Neighborhood Streets
Back Neighborhood Streets
-
Residential Streets
Back Residential Streets
-
Neighborhood Main Streets
Back Neighborhood Main Streets
-
Residential Streets
-
Avenues and Boulevards
Back Avenues and Boulevards
-
Central One-Way Streets
Back Central One-Way Streets
-
Central Two-Way Streets
Back Central Two-Way Streets
- Transit Streets
-
Large Streets with Transit
Back Large Streets with Transit
- Grand Streets
-
Central One-Way Streets
-
Special Conditions
Back Special Conditions
-
Elevated Structure Improvement
Back Elevated Structure Improvement
-
Elevated Structure Removal
Back Elevated Structure Removal
-
Streets to Streams
Back Streets to Streams
-
Temporary Street Closures
Back Temporary Street Closures
-
Post-Industrial Revitalization
Back Post-Industrial Revitalization
-
Waterfront and Parkside Streets
Back Waterfront and Parkside Streets
-
Historic Streets
Back Historic Streets
-
Elevated Structure Improvement
-
Streets in Informal Areas
Back Streets in Informal Areas
-
Intersections
Back Intersections
- Intersection Design Strategies
- Intersection Analysis
- Intersection Redesign
- Mini Roundabout
- Small Raised Intersection
- Neighborhood Gateway Intersection
- Intersection of Two-Way and One-Way Streets
- Major Intersection: Reclaiming the Corners
- Major Intersection: Squaring the Circle
- Major Intersection: Cycle Protection
- Complex Intersection: Adding Public Plazas
- Complex Intersection: Improving Traffic Circles
- Complex Intersection: Increasing Permeability
- Resources
- Guides & Publications
- Global Street Design Guide
- Intersections
- Major Intersection: Squaring the Circle
Major Intersection: Squaring the Circle
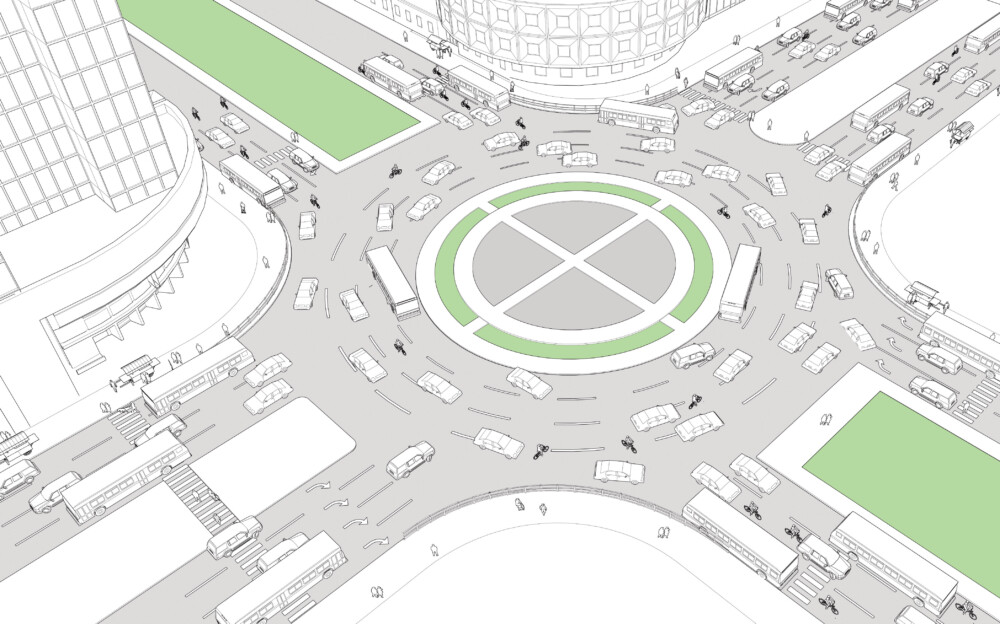
Existing Conditions
The illustration above depicts a wide, unsignalized intersection with a large, landscaped—but inaccessible—roundabout. Central medians divide the two-way traffic on both cross streets.
The large roundabout negates many of the benefits of a compact roundabout, such as managing speeds and reducing conflicts, given the large turning radii and minimal level of deflection required for moving vehicles.
This intersection creates an unbalanced allocation of space between modes.
The central space is difficult to access due to high traffic volumes and a lack of pedestrian crossings.
Pedestrian crossings are inconsistent and recessed from the intersection, increasing walking distances.

Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. A very wide traffic circle where the central space is naccessible. Pedestrians have to cover very long distances in order to cross the street due to the wide diameter of the traffic circle. Sites like this present a great opportunity for redesign.

Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam. A vulnerable user in a wheel chair tries to cross the street at a busy roundabout with no pedestrian crossings.
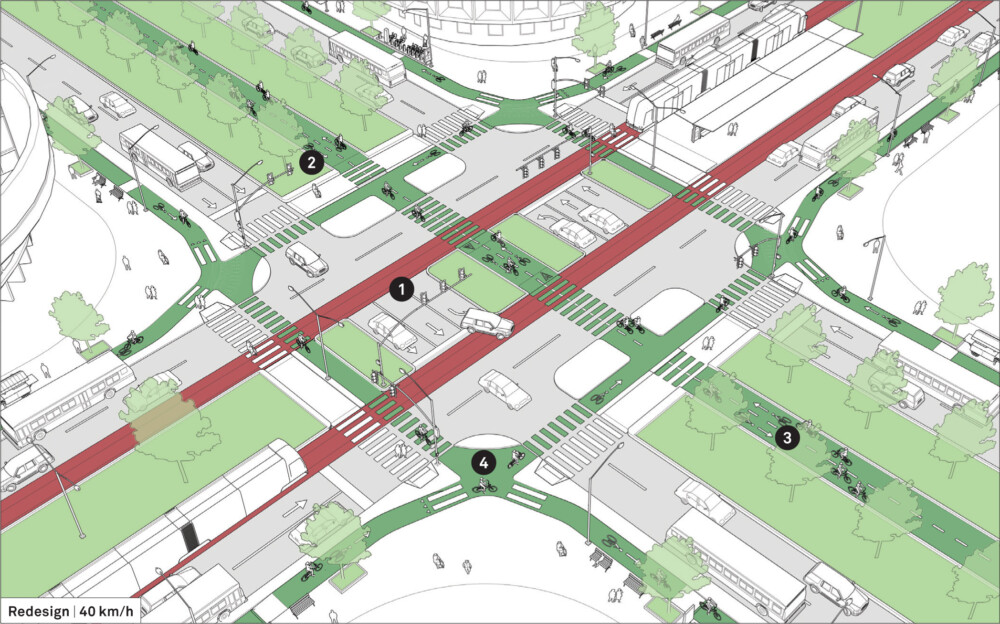
Design Guidance
This reconstructions shows the transformation of a roundabout into an orthogonal configuration with signalized traffic control and a more balanced allocation of space between different modes.
Reduce lane widths and add dedicated transit lanes, protected cycle facilities, and an improved walking environment.
Reduce corner radii to limit the speed of turning vehicles. Reclaim these corners for additional pedestrian space and to shorten crossing distances.
![]() Align the number of travel lanes through the intersection. Mark skip lines to direct users on continuous paths.
Align the number of travel lanes through the intersection. Mark skip lines to direct users on continuous paths.
Introduce dedicated, bidirectional transit facilities to reduce traffic congestion and increases total street capacity.
Ban turns that cross the transit lanes on unsignalized intersections.
![]() Take steps to activate wide central medians, which are valuable but underused public space. Use the wide median along the transit corridor for transit shelters and stations. Design refuge spaces to align with pedestrian crossings, to provide access to stations, and to offer seating opportunities recessed into landscape.
Take steps to activate wide central medians, which are valuable but underused public space. Use the wide median along the transit corridor for transit shelters and stations. Design refuge spaces to align with pedestrian crossings, to provide access to stations, and to offer seating opportunities recessed into landscape.
![]() A bidirectional cycle track is installed in the center median to create activity and utilize the space for mobility and recreational use. The cycle track is continuous, with a protected center crossing and access to side-running cycle tracks on either street.
A bidirectional cycle track is installed in the center median to create activity and utilize the space for mobility and recreational use. The cycle track is continuous, with a protected center crossing and access to side-running cycle tracks on either street.
![]() Protect cyclists by adding corner refuge islands and forward stop bars that make them more visible to oncoming and turning vehicles.
Protect cyclists by adding corner refuge islands and forward stop bars that make them more visible to oncoming and turning vehicles.
Wide medians should be landscaped and planted to increase permeability, water infiltration, shade, and biodiversity.

Bogota, Colombia. A bidirectional bike lane in the central median.
Adapted by Global Street Design Guide published by Island Press.
Next Section —