-
About Streets
- Introduction
- Defining Streets
-
Shaping Streets
- The Process of Shaping Streets
- Aligning with City and Regional Agendas
- Involving the Right Stakeholders
- Setting a Project Vision
- Communication and Engagement
- Costs and Budgets
- Phasing and Interim Strategies
- Coordination and Project Management
- Implementation and Materials
- Management
- Maintenance
- Institutionalizing Change
- Measuring and Evaluating Streets
-
Street Design Guidance
- Designing Streets for Great Cities
- Designing Streets for Place
-
Designing Streets for People
- Utilities and Infrastructure
- Operational and Management Strategies
- Design Controls
-
Street Transformations
- Streets
-
Intersections
- Intersection Design Strategies
- Intersection Analysis
- Intersection Redesign
- Mini Roundabout
- Small Raised Intersection
- Neighborhood Gateway Intersection
- Intersection of Two-Way and One-Way Streets
- Major Intersection: Reclaiming the Corners
- Major Intersection: Squaring the Circle
- Major Intersection: Cycle Protection
- Complex Intersection: Adding Public Plazas
- Complex Intersection: Improving Traffic Circles
- Complex Intersection: Increasing Permeability
- Resources
Global Street Design Guide
-
About Streets
- Introduction
- Defining Streets
-
Shaping Streets
Back Shaping Streets
- The Process of Shaping Streets
- Aligning with City and Regional Agendas
- Involving the Right Stakeholders
- Setting a Project Vision
- Communication and Engagement
- Costs and Budgets
- Phasing and Interim Strategies
- Coordination and Project Management
- Implementation and Materials
- Management
- Maintenance
- Institutionalizing Change
-
Measuring and Evaluating Streets
Back Measuring and Evaluating Streets
-
Street Design Guidance
-
Designing Streets for Great Cities
Back Designing Streets for Great Cities
-
Designing Streets for Place
Back Designing Streets for Place
-
Designing Streets for People
Back Designing Streets for People
- Comparing Street Users
- A Variety of Street Users
-
Designing for Pedestrians
Back Designing for Pedestrians
- Designing for Cyclists
-
Designing for Transit Riders
Back Designing for Transit Riders
- Overview
- Transit Networks
- Transit Toolbox
-
Transit Facilities
Back Transit Facilities
-
Transit Stops
Back Transit Stops
-
Additional Guidance
Back Additional Guidance
-
Designing for Motorists
Back Designing for Motorists
-
Designing for Freight and Service Operators
Back Designing for Freight and Service Operators
-
Designing for People Doing Business
Back Designing for People Doing Business
-
Utilities and Infrastructure
Back Utilities and Infrastructure
- Utilities
-
Green Infrastructure and Stormwater Management
Back Green Infrastructure and Stormwater Management
-
Lighting and Technology
Back Lighting and Technology
-
Operational and Management Strategies
Back Operational and Management Strategies
- Design Controls
-
Street Transformations
-
Streets
Back Streets
- Street Design Strategies
- Street Typologies
-
Pedestrian-Priority Spaces
Back Pedestrian-Priority Spaces
-
Pedestrian-Only Streets
Back Pedestrian-Only Streets
-
Laneways and Alleys
Back Laneways and Alleys
- Parklets
-
Pedestrian Plazas
Back Pedestrian Plazas
-
Pedestrian-Only Streets
-
Shared Streets
Back Shared Streets
-
Commercial Shared Streets
Back Commercial Shared Streets
-
Residential Shared Streets
Back Residential Shared Streets
-
Commercial Shared Streets
-
Neighborhood Streets
Back Neighborhood Streets
-
Residential Streets
Back Residential Streets
-
Neighborhood Main Streets
Back Neighborhood Main Streets
-
Residential Streets
-
Avenues and Boulevards
Back Avenues and Boulevards
-
Central One-Way Streets
Back Central One-Way Streets
-
Central Two-Way Streets
Back Central Two-Way Streets
- Transit Streets
-
Large Streets with Transit
Back Large Streets with Transit
- Grand Streets
-
Central One-Way Streets
-
Special Conditions
Back Special Conditions
-
Elevated Structure Improvement
Back Elevated Structure Improvement
-
Elevated Structure Removal
Back Elevated Structure Removal
-
Streets to Streams
Back Streets to Streams
-
Temporary Street Closures
Back Temporary Street Closures
-
Post-Industrial Revitalization
Back Post-Industrial Revitalization
-
Waterfront and Parkside Streets
Back Waterfront and Parkside Streets
-
Historic Streets
Back Historic Streets
-
Elevated Structure Improvement
-
Streets in Informal Areas
Back Streets in Informal Areas
-
Intersections
Back Intersections
- Intersection Design Strategies
- Intersection Analysis
- Intersection Redesign
- Mini Roundabout
- Small Raised Intersection
- Neighborhood Gateway Intersection
- Intersection of Two-Way and One-Way Streets
- Major Intersection: Reclaiming the Corners
- Major Intersection: Squaring the Circle
- Major Intersection: Cycle Protection
- Complex Intersection: Adding Public Plazas
- Complex Intersection: Improving Traffic Circles
- Complex Intersection: Increasing Permeability
- Resources
- Guides & Publications
- Global Street Design Guide
- Streets
- Avenues and Boulevards
- Large Streets with Transit
- Example 2: 38 m
Example 2: 38 m
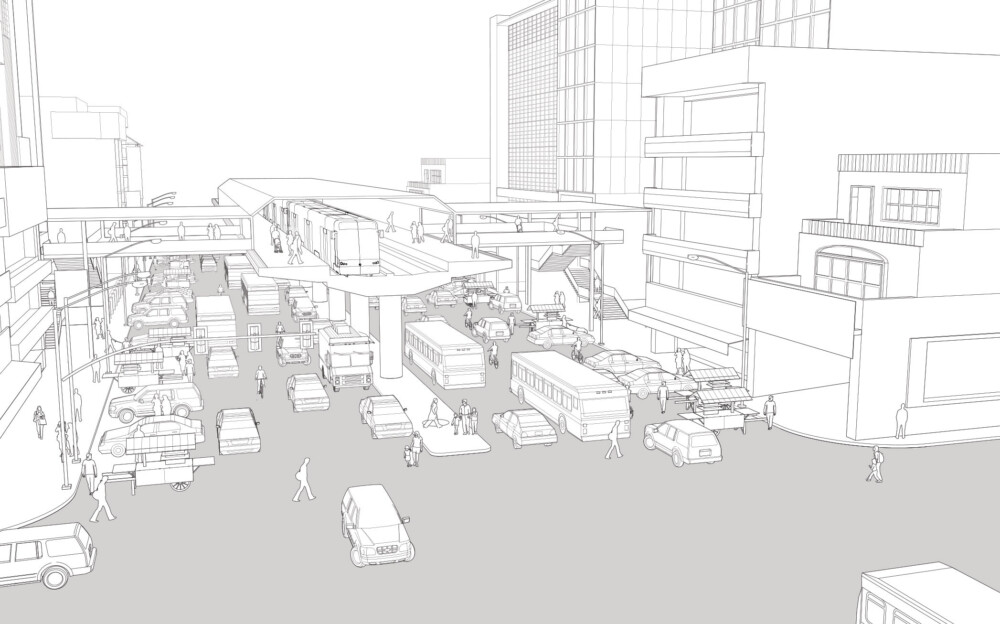
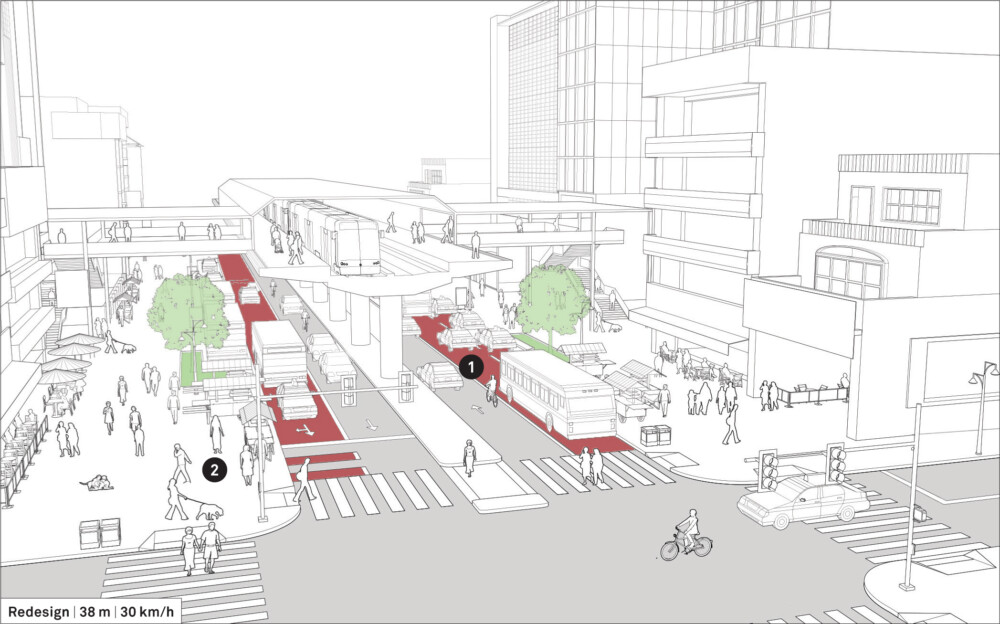
Existing Conditions
This street depicted in the illustration above has elevated transit infrastructure. It provides regional connectivity and a variety of collective transit options. The elevated transit stop serves as a multimodal exchange point, but at-grade collective transport has poor reliability due to shared travel lanes and heavy congestion.
Collective transport passengers are faced with poorly marked stops and disorienting transfer spaces.
Undefined areas along the sidewalks are occupied by street vendors, rickshaws, and unregulated car and motorcycle parking that force pedestrians onto the roadbed.
High speeds, long crossing distances without clear markings, and narrow, non-continuous, and inaccessible sidewalks create an unsafe pedestrian environment.
Utilities and elevated transit infrastructure often block clear pedestrian paths and limit visibility.

Paris, France
Design Guidance
The street is redesigned to prioritize transit and shared mobility, improve walking conditions and public space, and transform key transfer nodes into recognizable landmarks.
![]() Eliminate excess traffic lanes and designate a curbside transit lane in each direction. Marked transit lanes may be shared with taxis and small collective transport. To ensure smooth operation of collective transport services, provide pull-in and drop-off stops for boarding, which allows other transit vehicles to pass. These alternate with accessible parking spaces and taxi stands. See: Transit Facilities.
Eliminate excess traffic lanes and designate a curbside transit lane in each direction. Marked transit lanes may be shared with taxis and small collective transport. To ensure smooth operation of collective transport services, provide pull-in and drop-off stops for boarding, which allows other transit vehicles to pass. These alternate with accessible parking spaces and taxi stands. See: Transit Facilities.
Widen sidewalks and provide universal accessibility to better serve the needs of heavy pedestrian volumes.
![]() Extend the curb to create dedicated areas for vendors in the same zone as pull-in lanes, ensuring a clear path for pedestrians.
Extend the curb to create dedicated areas for vendors in the same zone as pull-in lanes, ensuring a clear path for pedestrians.
Extend the central median to create pedestrian refuge islands. See: Pedestrian Refuges.
Provide signage and wayfinding for transit stops to help navigate the users and to identify transit routes.
Add street furniture and trees to provide a comfortable street environment. See: Pedestrian Toolbox.

Chengdu, China
Adapted by Global Street Design Guide published by Island Press.
Next Section —