-
About Streets
- Introduction
- Defining Streets
-
Shaping Streets
- The Process of Shaping Streets
- Aligning with City and Regional Agendas
- Involving the Right Stakeholders
- Setting a Project Vision
- Communication and Engagement
- Costs and Budgets
- Phasing and Interim Strategies
- Coordination and Project Management
- Implementation and Materials
- Management
- Maintenance
- Institutionalizing Change
- Measuring and Evaluating Streets
-
Street Design Guidance
- Designing Streets for Great Cities
- Designing Streets for Place
-
Designing Streets for People
- Utilities and Infrastructure
- Operational and Management Strategies
- Design Controls
-
Street Transformations
- Streets
-
Intersections
- Intersection Design Strategies
- Intersection Analysis
- Intersection Redesign
- Mini Roundabout
- Small Raised Intersection
- Neighborhood Gateway Intersection
- Intersection of Two-Way and One-Way Streets
- Major Intersection: Reclaiming the Corners
- Major Intersection: Squaring the Circle
- Major Intersection: Cycle Protection
- Complex Intersection: Adding Public Plazas
- Complex Intersection: Improving Traffic Circles
- Complex Intersection: Increasing Permeability
- Resources
Global Street Design Guide
-
About Streets
- Introduction
- Defining Streets
-
Shaping Streets
Back Shaping Streets
- The Process of Shaping Streets
- Aligning with City and Regional Agendas
- Involving the Right Stakeholders
- Setting a Project Vision
- Communication and Engagement
- Costs and Budgets
- Phasing and Interim Strategies
- Coordination and Project Management
- Implementation and Materials
- Management
- Maintenance
- Institutionalizing Change
-
Measuring and Evaluating Streets
Back Measuring and Evaluating Streets
-
Street Design Guidance
-
Designing Streets for Great Cities
Back Designing Streets for Great Cities
-
Designing Streets for Place
Back Designing Streets for Place
-
Designing Streets for People
Back Designing Streets for People
- Comparing Street Users
- A Variety of Street Users
-
Designing for Pedestrians
Back Designing for Pedestrians
- Designing for Cyclists
-
Designing for Transit Riders
Back Designing for Transit Riders
- Overview
- Transit Networks
- Transit Toolbox
-
Transit Facilities
Back Transit Facilities
-
Transit Stops
Back Transit Stops
-
Additional Guidance
Back Additional Guidance
-
Designing for Motorists
Back Designing for Motorists
-
Designing for Freight and Service Operators
Back Designing for Freight and Service Operators
-
Designing for People Doing Business
Back Designing for People Doing Business
-
Utilities and Infrastructure
Back Utilities and Infrastructure
- Utilities
-
Green Infrastructure and Stormwater Management
Back Green Infrastructure and Stormwater Management
-
Lighting and Technology
Back Lighting and Technology
-
Operational and Management Strategies
Back Operational and Management Strategies
- Design Controls
-
Street Transformations
-
Streets
Back Streets
- Street Design Strategies
- Street Typologies
-
Pedestrian-Priority Spaces
Back Pedestrian-Priority Spaces
-
Pedestrian-Only Streets
Back Pedestrian-Only Streets
-
Laneways and Alleys
Back Laneways and Alleys
- Parklets
-
Pedestrian Plazas
Back Pedestrian Plazas
-
Pedestrian-Only Streets
-
Shared Streets
Back Shared Streets
-
Commercial Shared Streets
Back Commercial Shared Streets
-
Residential Shared Streets
Back Residential Shared Streets
-
Commercial Shared Streets
-
Neighborhood Streets
Back Neighborhood Streets
-
Residential Streets
Back Residential Streets
-
Neighborhood Main Streets
Back Neighborhood Main Streets
-
Residential Streets
-
Avenues and Boulevards
Back Avenues and Boulevards
-
Central One-Way Streets
Back Central One-Way Streets
-
Central Two-Way Streets
Back Central Two-Way Streets
- Transit Streets
-
Large Streets with Transit
Back Large Streets with Transit
- Grand Streets
-
Central One-Way Streets
-
Special Conditions
Back Special Conditions
-
Elevated Structure Improvement
Back Elevated Structure Improvement
-
Elevated Structure Removal
Back Elevated Structure Removal
-
Streets to Streams
Back Streets to Streams
-
Temporary Street Closures
Back Temporary Street Closures
-
Post-Industrial Revitalization
Back Post-Industrial Revitalization
-
Waterfront and Parkside Streets
Back Waterfront and Parkside Streets
-
Historic Streets
Back Historic Streets
-
Elevated Structure Improvement
-
Streets in Informal Areas
Back Streets in Informal Areas
-
Intersections
Back Intersections
- Intersection Design Strategies
- Intersection Analysis
- Intersection Redesign
- Mini Roundabout
- Small Raised Intersection
- Neighborhood Gateway Intersection
- Intersection of Two-Way and One-Way Streets
- Major Intersection: Reclaiming the Corners
- Major Intersection: Squaring the Circle
- Major Intersection: Cycle Protection
- Complex Intersection: Adding Public Plazas
- Complex Intersection: Improving Traffic Circles
- Complex Intersection: Increasing Permeability
- Resources
- Guides & Publications
- Global Street Design Guide
- Streets
- Avenues and Boulevards
- Central Two-Way Streets
- Example 3: 40 m
Example 3: 40 m
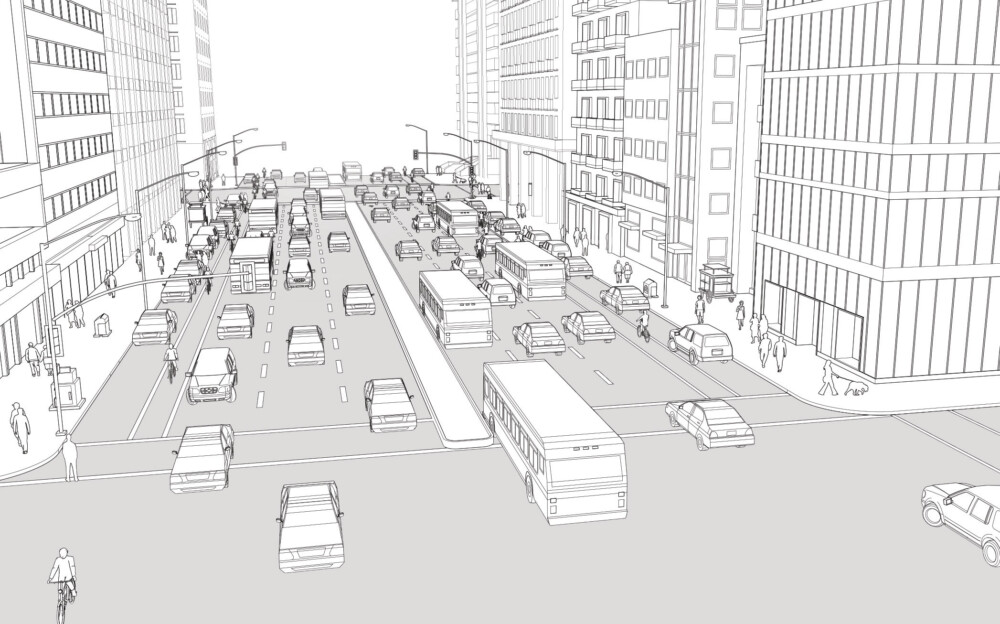
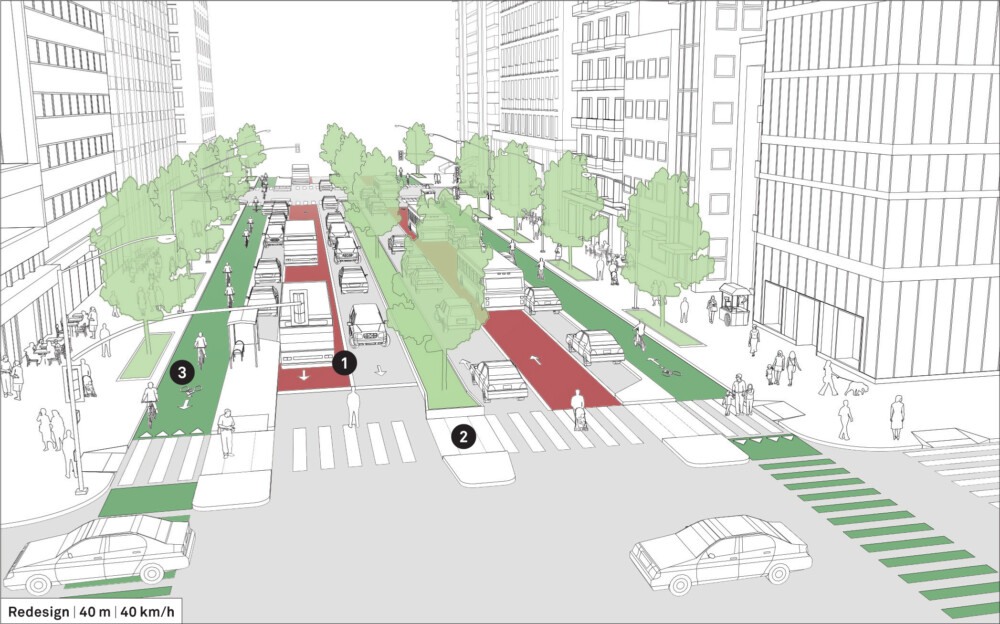
Existing Conditions
The illustration above depicts a large two-way street in the center of the city, used both as a thoroughfare and as a destination with a mix of programs. Wide travel lanes encourage speeding and create an unsafe walking and cycling environment.
Cross-traffic turns are a frequent source of conflict, resulting in head-on collisions between motorists and pedestrians or cyclists.
Cyclists feel unsafe riding on narrow cycle lanes located between fast-moving traffic and the curbside parking car door zone. Double-parked vehicles and cars getting into the parking lane may force cyclists to suddenly divert into the adjacent travel lane at great risk.
Wide medians act as an undefined refuge island, creating a pause point in the middle of the street with no protection. Heavy turn volumes and large corner radii at the intersections result in high-speed turns that put pedestrians and cyclists in danger.

Singapore, Singapore
Design Guidance
![]() Redesign large streets to accommodate both through- and destination-oriented traffic. Give priority to movement of high occupancy vehicles, like mass transit, van-pools, and taxis, to increase the street’s capacity.
Redesign large streets to accommodate both through- and destination-oriented traffic. Give priority to movement of high occupancy vehicles, like mass transit, van-pools, and taxis, to increase the street’s capacity.
Add dedicated transit lanes and enable in-lane transit stops using bulbs or islands. See: Transit Stops.
If transit frequency is low, consider allowing taxis and other means of collective transport in these lanes to increase the movement capacity.
![]() Widen the central median at the intersection and at transit stops to create refuge islands. Refuge islands, when paired with curb extensions at parking spaces, help in reducing time and crossing distances for pedestrians.
Widen the central median at the intersection and at transit stops to create refuge islands. Refuge islands, when paired with curb extensions at parking spaces, help in reducing time and crossing distances for pedestrians.
Widen sidewalks to provide universal access, add green infrastructure, and increase space for pedestrians and commercial activity.
![]() Reduce travel lanes and add parking protected cycle tracks in each direction.
Reduce travel lanes and add parking protected cycle tracks in each direction.
Side-running directional cycle tracks allow easy and convenient access for cyclists. See: Cycle Facilities.
Restrict freight delivery or encourage off peak delivery to eliminate double-parking obstructions. See: Design Hour.
Support new configurations and traffic patterns through education campaigns and proactive enforcement. Allow users time to adjust to significant transformations.
Add landscaping to provide shade and greenery, with potential to supplement stormwater management. These additions may also help attract new businesses.

Seattle, USA
Adapted by Global Street Design Guide published by Island Press.
Next Section —