-
About Streets
- Introduction
- Defining Streets
-
Shaping Streets
- The Process of Shaping Streets
- Aligning with City and Regional Agendas
- Involving the Right Stakeholders
- Setting a Project Vision
- Communication and Engagement
- Costs and Budgets
- Phasing and Interim Strategies
- Coordination and Project Management
- Implementation and Materials
- Management
- Maintenance
- Institutionalizing Change
- Measuring and Evaluating Streets
-
Street Design Guidance
- Designing Streets for Great Cities
- Designing Streets for Place
-
Designing Streets for People
- Utilities and Infrastructure
- Operational and Management Strategies
- Design Controls
-
Street Transformations
- Streets
-
Intersections
- Intersection Design Strategies
- Intersection Analysis
- Intersection Redesign
- Mini Roundabout
- Small Raised Intersection
- Neighborhood Gateway Intersection
- Intersection of Two-Way and One-Way Streets
- Major Intersection: Reclaiming the Corners
- Major Intersection: Squaring the Circle
- Major Intersection: Cycle Protection
- Complex Intersection: Adding Public Plazas
- Complex Intersection: Improving Traffic Circles
- Complex Intersection: Increasing Permeability
- Resources
Global Street Design Guide
-
About Streets
- Introduction
- Defining Streets
-
Shaping Streets
Back Shaping Streets
- The Process of Shaping Streets
- Aligning with City and Regional Agendas
- Involving the Right Stakeholders
- Setting a Project Vision
- Communication and Engagement
- Costs and Budgets
- Phasing and Interim Strategies
- Coordination and Project Management
- Implementation and Materials
- Management
- Maintenance
- Institutionalizing Change
-
Measuring and Evaluating Streets
Back Measuring and Evaluating Streets
-
Street Design Guidance
-
Designing Streets for Great Cities
Back Designing Streets for Great Cities
-
Designing Streets for Place
Back Designing Streets for Place
-
Designing Streets for People
Back Designing Streets for People
- Comparing Street Users
- A Variety of Street Users
-
Designing for Pedestrians
Back Designing for Pedestrians
- Designing for Cyclists
-
Designing for Transit Riders
Back Designing for Transit Riders
- Overview
- Transit Networks
- Transit Toolbox
-
Transit Facilities
Back Transit Facilities
-
Transit Stops
Back Transit Stops
-
Additional Guidance
Back Additional Guidance
-
Designing for Motorists
Back Designing for Motorists
-
Designing for Freight and Service Operators
Back Designing for Freight and Service Operators
-
Designing for People Doing Business
Back Designing for People Doing Business
-
Utilities and Infrastructure
Back Utilities and Infrastructure
- Utilities
-
Green Infrastructure and Stormwater Management
Back Green Infrastructure and Stormwater Management
-
Lighting and Technology
Back Lighting and Technology
-
Operational and Management Strategies
Back Operational and Management Strategies
- Design Controls
-
Street Transformations
-
Streets
Back Streets
- Street Design Strategies
- Street Typologies
-
Pedestrian-Priority Spaces
Back Pedestrian-Priority Spaces
-
Pedestrian-Only Streets
Back Pedestrian-Only Streets
-
Laneways and Alleys
Back Laneways and Alleys
- Parklets
-
Pedestrian Plazas
Back Pedestrian Plazas
-
Pedestrian-Only Streets
-
Shared Streets
Back Shared Streets
-
Commercial Shared Streets
Back Commercial Shared Streets
-
Residential Shared Streets
Back Residential Shared Streets
-
Commercial Shared Streets
-
Neighborhood Streets
Back Neighborhood Streets
-
Residential Streets
Back Residential Streets
-
Neighborhood Main Streets
Back Neighborhood Main Streets
-
Residential Streets
-
Avenues and Boulevards
Back Avenues and Boulevards
-
Central One-Way Streets
Back Central One-Way Streets
-
Central Two-Way Streets
Back Central Two-Way Streets
- Transit Streets
-
Large Streets with Transit
Back Large Streets with Transit
- Grand Streets
-
Central One-Way Streets
-
Special Conditions
Back Special Conditions
-
Elevated Structure Improvement
Back Elevated Structure Improvement
-
Elevated Structure Removal
Back Elevated Structure Removal
-
Streets to Streams
Back Streets to Streams
-
Temporary Street Closures
Back Temporary Street Closures
-
Post-Industrial Revitalization
Back Post-Industrial Revitalization
-
Waterfront and Parkside Streets
Back Waterfront and Parkside Streets
-
Historic Streets
Back Historic Streets
-
Elevated Structure Improvement
-
Streets in Informal Areas
Back Streets in Informal Areas
-
Intersections
Back Intersections
- Intersection Design Strategies
- Intersection Analysis
- Intersection Redesign
- Mini Roundabout
- Small Raised Intersection
- Neighborhood Gateway Intersection
- Intersection of Two-Way and One-Way Streets
- Major Intersection: Reclaiming the Corners
- Major Intersection: Squaring the Circle
- Major Intersection: Cycle Protection
- Complex Intersection: Adding Public Plazas
- Complex Intersection: Improving Traffic Circles
- Complex Intersection: Increasing Permeability
- Resources
- Guides & Publications
- Global Street Design Guide
- Streets
- Avenues and Boulevards
- Central Two-Way Streets
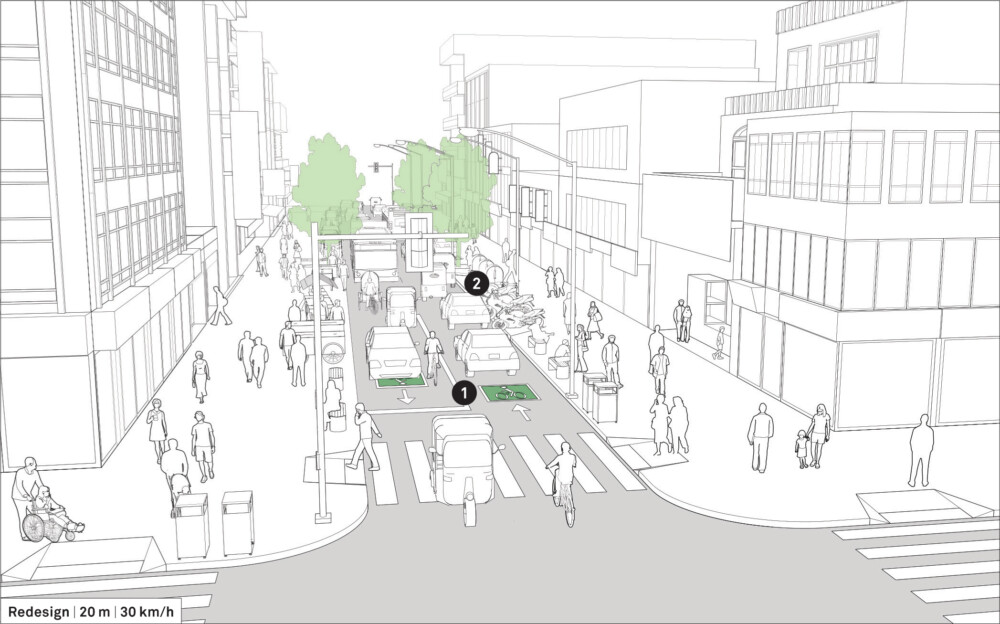
- Example 1: 20 m
Example 1: 20 m
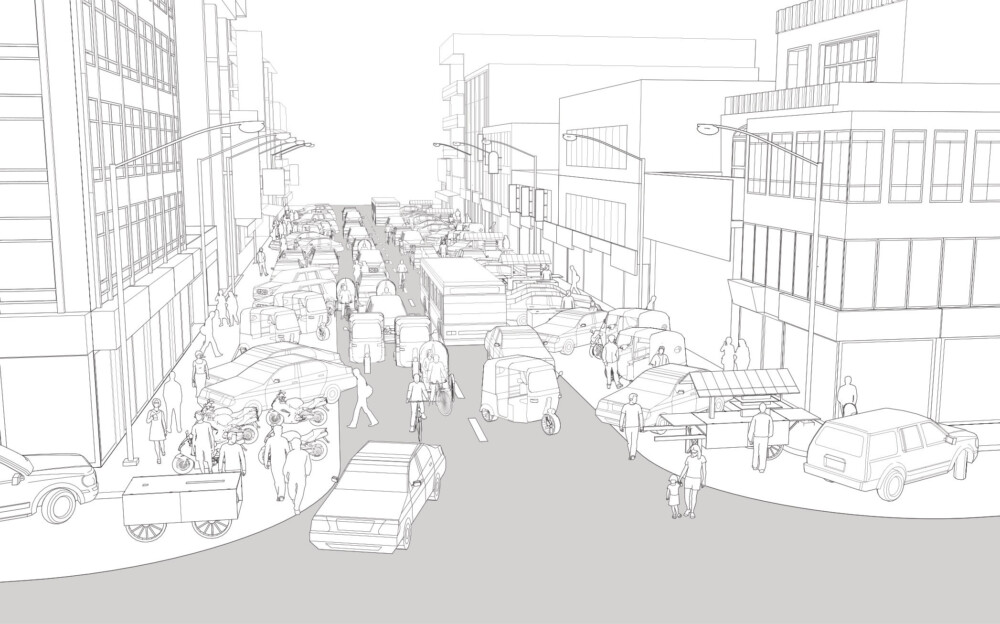

Existing Conditions
The illustration above depicts a one-way street that was not originally designed for motorized traffic. This street type might have moderate traffic volumes, and its high-pedestrian activity might spill onto the roadbed.
Pedestrians are subject to extreme danger due to motor vehicle speeding, and inaccessible, narrow, and discontinuous sidewalks that are often obstructed by utilities or parked cars.
Minimal road markings lead pedestrians to cross the street in undefined and unsafe zones.
Unregulated angled curbside parking and street vendors encroach upon pedestrian space and travel lanes.

Cairo, Egypt
Design Guidance
![]() Convert the one-way street into a two-way street with one travel lane in each direction. Bidirectional travel reduces vehicular speeding as drivers must be cautious and aware of the oncoming traffic. See: Travel Lanes.
Convert the one-way street into a two-way street with one travel lane in each direction. Bidirectional travel reduces vehicular speeding as drivers must be cautious and aware of the oncoming traffic. See: Travel Lanes.
Two-way streets increase overall network connectivity but intersections must be carefully designed to minimize conflicts. Mitigate turn conflicts using tight corner radii, leading pedestrian intervals, and turn prohibitions for motor vehicles.
Replace angled parking with regulated curbside parking to provide increased space for sidewalks.
Widen sidewalks to accommodate trees, utilities, and commercial activity while ensuring a clear pedestrian path.
Install curb extensions to shorten pedestrian crossing distances and improve sightlines; lengthening the curb extension creates new public space for curbside amenities and street vendors. See: Sidewalk Extensions.
![]() Use curbside parking lanes that are flexible zones to accommodate boarding for small collective transit and taxis, dedicated cycle or motorcycle parking, and tree pits.
Use curbside parking lanes that are flexible zones to accommodate boarding for small collective transit and taxis, dedicated cycle or motorcycle parking, and tree pits.
Create a safer people-centered environment with sidewalk-aligned crosswalks, visible and legible markings, and added public amenities.
Improved pedestrian zones and drop-off areas are beneficial to local business establishments.

New York City, USA
Adapted by Global Street Design Guide published by Island Press.
Next Section —