-
About Streets
- Introduction
- Defining Streets
-
Shaping Streets
- The Process of Shaping Streets
- Aligning with City and Regional Agendas
- Involving the Right Stakeholders
- Setting a Project Vision
- Communication and Engagement
- Costs and Budgets
- Phasing and Interim Strategies
- Coordination and Project Management
- Implementation and Materials
- Management
- Maintenance
- Institutionalizing Change
- Measuring and Evaluating Streets
-
Street Design Guidance
- Designing Streets for Great Cities
- Designing Streets for Place
-
Designing Streets for People
- Utilities and Infrastructure
- Operational and Management Strategies
- Design Controls
-
Street Transformations
- Streets
-
Intersections
- Intersection Design Strategies
- Intersection Analysis
- Intersection Redesign
- Mini Roundabout
- Small Raised Intersection
- Neighborhood Gateway Intersection
- Intersection of Two-Way and One-Way Streets
- Major Intersection: Reclaiming the Corners
- Major Intersection: Squaring the Circle
- Major Intersection: Cycle Protection
- Complex Intersection: Adding Public Plazas
- Complex Intersection: Improving Traffic Circles
- Complex Intersection: Increasing Permeability
- Resources
Global Street Design Guide
-
About Streets
- Introduction
- Defining Streets
-
Shaping Streets
Back Shaping Streets
- The Process of Shaping Streets
- Aligning with City and Regional Agendas
- Involving the Right Stakeholders
- Setting a Project Vision
- Communication and Engagement
- Costs and Budgets
- Phasing and Interim Strategies
- Coordination and Project Management
- Implementation and Materials
- Management
- Maintenance
- Institutionalizing Change
-
Measuring and Evaluating Streets
Back Measuring and Evaluating Streets
-
Street Design Guidance
-
Designing Streets for Great Cities
Back Designing Streets for Great Cities
-
Designing Streets for Place
Back Designing Streets for Place
-
Designing Streets for People
Back Designing Streets for People
- Comparing Street Users
- A Variety of Street Users
-
Designing for Pedestrians
Back Designing for Pedestrians
- Designing for Cyclists
-
Designing for Transit Riders
Back Designing for Transit Riders
- Overview
- Transit Networks
- Transit Toolbox
-
Transit Facilities
Back Transit Facilities
-
Transit Stops
Back Transit Stops
-
Additional Guidance
Back Additional Guidance
-
Designing for Motorists
Back Designing for Motorists
-
Designing for Freight and Service Operators
Back Designing for Freight and Service Operators
-
Designing for People Doing Business
Back Designing for People Doing Business
-
Utilities and Infrastructure
Back Utilities and Infrastructure
- Utilities
-
Green Infrastructure and Stormwater Management
Back Green Infrastructure and Stormwater Management
-
Lighting and Technology
Back Lighting and Technology
-
Operational and Management Strategies
Back Operational and Management Strategies
- Design Controls
-
Street Transformations
-
Streets
Back Streets
- Street Design Strategies
- Street Typologies
-
Pedestrian-Priority Spaces
Back Pedestrian-Priority Spaces
-
Pedestrian-Only Streets
Back Pedestrian-Only Streets
-
Laneways and Alleys
Back Laneways and Alleys
- Parklets
-
Pedestrian Plazas
Back Pedestrian Plazas
-
Pedestrian-Only Streets
-
Shared Streets
Back Shared Streets
-
Commercial Shared Streets
Back Commercial Shared Streets
-
Residential Shared Streets
Back Residential Shared Streets
-
Commercial Shared Streets
-
Neighborhood Streets
Back Neighborhood Streets
-
Residential Streets
Back Residential Streets
-
Neighborhood Main Streets
Back Neighborhood Main Streets
-
Residential Streets
-
Avenues and Boulevards
Back Avenues and Boulevards
-
Central One-Way Streets
Back Central One-Way Streets
-
Central Two-Way Streets
Back Central Two-Way Streets
- Transit Streets
-
Large Streets with Transit
Back Large Streets with Transit
- Grand Streets
-
Central One-Way Streets
-
Special Conditions
Back Special Conditions
-
Elevated Structure Improvement
Back Elevated Structure Improvement
-
Elevated Structure Removal
Back Elevated Structure Removal
-
Streets to Streams
Back Streets to Streams
-
Temporary Street Closures
Back Temporary Street Closures
-
Post-Industrial Revitalization
Back Post-Industrial Revitalization
-
Waterfront and Parkside Streets
Back Waterfront and Parkside Streets
-
Historic Streets
Back Historic Streets
-
Elevated Structure Improvement
-
Streets in Informal Areas
Back Streets in Informal Areas
-
Intersections
Back Intersections
- Intersection Design Strategies
- Intersection Analysis
- Intersection Redesign
- Mini Roundabout
- Small Raised Intersection
- Neighborhood Gateway Intersection
- Intersection of Two-Way and One-Way Streets
- Major Intersection: Reclaiming the Corners
- Major Intersection: Squaring the Circle
- Major Intersection: Cycle Protection
- Complex Intersection: Adding Public Plazas
- Complex Intersection: Improving Traffic Circles
- Complex Intersection: Increasing Permeability
- Resources
- Guides & Publications
- Global Street Design Guide
- Streets
- Avenues and Boulevards
- Grand Streets
- Example 1: 52 m
Example 1: 52 m
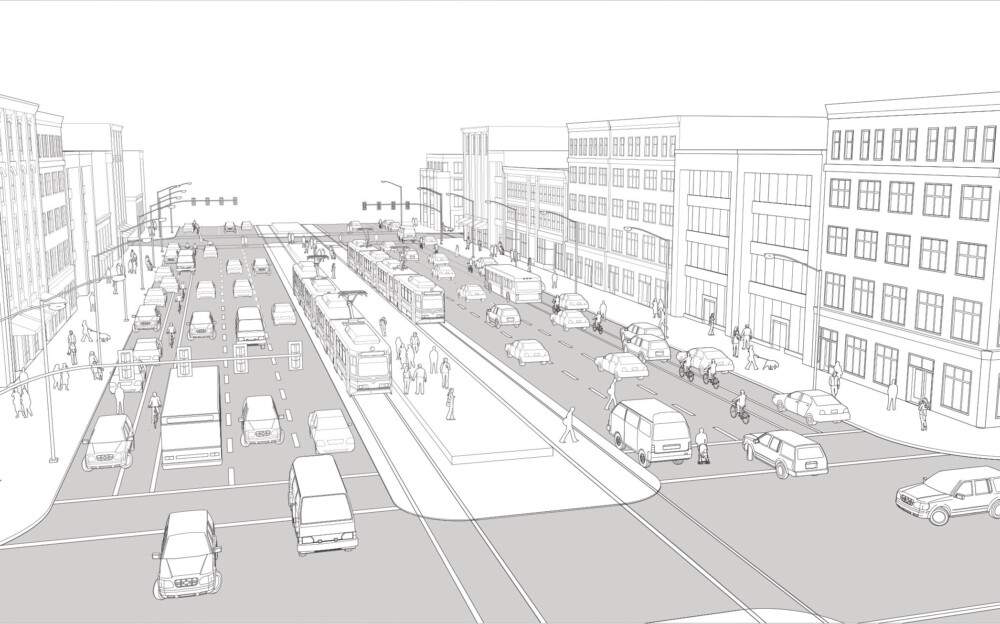
Existing Conditions
The illustration above depicts a major street with center-running transit and unprotected cycle lanes. It serves as an arterial corridor with three wide lanes for fast-moving traffic in each direction. This street connects the city across multiple neighborhoods and regionally.
Safety issues for vulnerable users are increased by long crosswalk distances and poorly defined and recessed crosswalks that increase crossing time.
Sidewalks are wide. However, a lack of landscaping and ground-level activities render them uninviting and dull spaces.
Center-running and center-loading mass transit has restricted entry and exit points. Stops might lack proper accessibility features.
Double-parked freight vehicles create weaving conflicts and safety hazards at peak hours for motorists and cyclists.
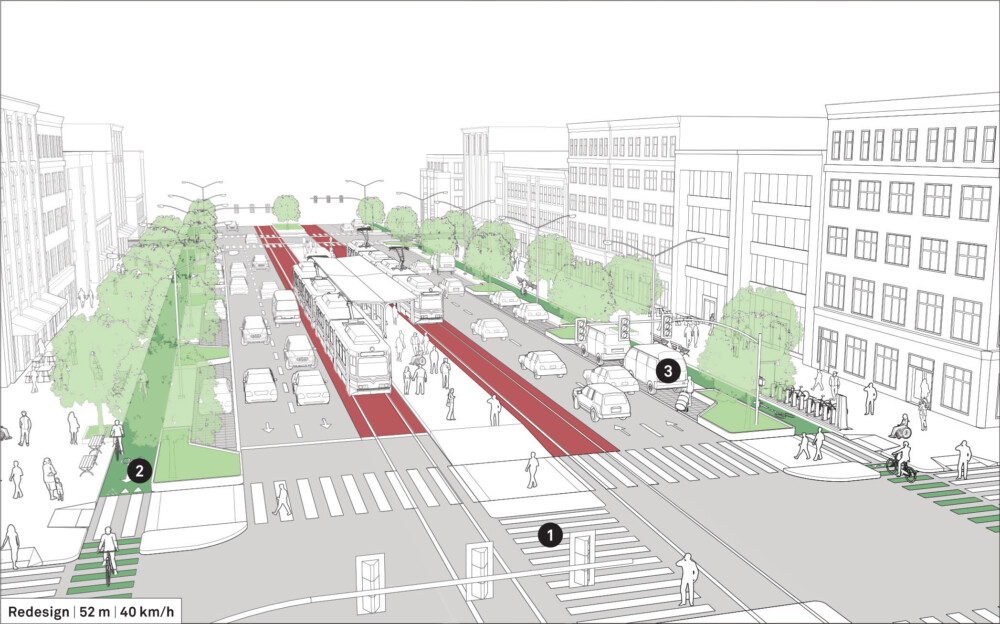
Design Guidance
Delineate and demarcate different modes to efficiently share and manage the street.
Enhance the centre-running transit lanes through distinct paving or color treatments. Provide level boarding platforms, accessible ramps and paths, as well as audible and tactile features.
![]() Add controlled mid-block crossings at transit stops to facilitate safe crossing from both sides of the street. Cover transit stops to provide a sheltered and comfortable waiting space.
Add controlled mid-block crossings at transit stops to facilitate safe crossing from both sides of the street. Cover transit stops to provide a sheltered and comfortable waiting space.
Install refuge islands on the central median and curb extensions to shorten the overall crossing distance.
Encourage commercial activity and street vendors on wide sidewalks. Add street furniture and landscaping while maintaining a continuous pedestrian clear path.
![]() Replace one travel lane in each direction with a parking-protected cycle track to encourage cycling as a healthy and sustainable mobility choice. Cycle share stations may be sited adjacent to cycle tracks and near transit stations to accommodate first- and last-mile trips.
Replace one travel lane in each direction with a parking-protected cycle track to encourage cycling as a healthy and sustainable mobility choice. Cycle share stations may be sited adjacent to cycle tracks and near transit stations to accommodate first- and last-mile trips.
Install street trees and green infrastructure along parking-side medians to dissipate road noise, manage stormwater run-off, and improve the urban environment.
![]() Provide loading zones at strategic locations within the parking strip. Restrict freight delivery or encourage off-peak delivery to eliminate double parking obstructions. See: Designing for Freight and Service Operators.
Provide loading zones at strategic locations within the parking strip. Restrict freight delivery or encourage off-peak delivery to eliminate double parking obstructions. See: Designing for Freight and Service Operators.

Antwerp, Belgium

Barcelona, Spain
Adapted by Global Street Design Guide published by Island Press.
Next Section —